
 The
staff
The
staff
 Report
1993 (postscript file, 255K)
Report
1993 (postscript file, 255K)
 Report
1994
(postscript file, 56K)
Report
1994
(postscript file, 56K)
 Report
1995 (document
html)
Report
1995 (document
html)
 Report
1996
(postscript file, 57K)
Report
1996
(postscript file, 57K)
 Le
bilan (14 slides, postscript file, 381K)
Le
bilan (14 slides, postscript file, 381K)
 Report
1997
(postscript file, 67K)
Report
1997
(postscript file, 67K)
What we do now :
 Our involvment in the SINUS
project
Our involvment in the SINUS
project
 The
SHOOD software
The
SHOOD software
The SHOOD software is an object-based knowledge representation system.
It allows the modelling of active, composite, evolving, incomplete and
partially inconsistent objects. The target applications include concurrent
engineering and integrated design. It is available for research and academic
institutions for non-commercial use.
CAST is a software integration platform. It allows the specification, deployment and execution of distributed collaborative applications and code-coupling.
CAST allows the specification of user applications defined by collections of distributed cooperating components. They are synchronised by a set of choice, delay, iteration, parallel, and sequence operators. CAST relies on a formal specification formalism and a high-level graphic interface.


 CAST is a software integration platform.
It is used for numeric simulation codes integration in the european
DECISION
project : "Integrated Optimization Strategies for Increased Engineering
Design Complexity" (Esprit project HPCN : EP25058, october 1997-april
2000).
CAST is a software integration platform.
It is used for numeric simulation codes integration in the european
DECISION
project : "Integrated Optimization Strategies for Increased Engineering
Design Complexity" (Esprit project HPCN : EP25058, october 1997-april
2000).
The other project partners are Dassault-Aviation (coordinator), NAG (G.B), MESSET (Finland), VTT (Finland), NOKKA-TUME (Finland) and the University of Jyvaskyla (Finland).

The goal is to develop an integration platform for distributed applications
in multi-discipline optimisation problems for complex engineering projects.
An example is the code-coupling for combined aerodynamics and structure
optimisation in aerospace design.
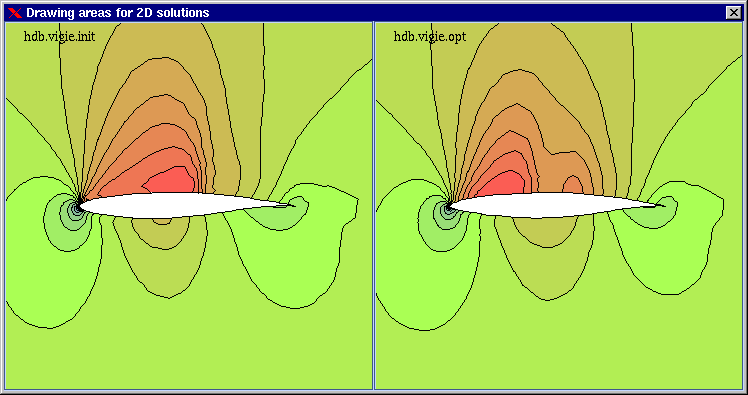
This project triggered a tight cooperation with the SINUS project (Simulation Numerique pour les Sciences de l'ingenieur) at INRIA Sophia-Antipolis. The CAST platform integrates for example optimisation modules developed by the SINUS project, which are based on genetic algorithms, with aerodynamics simulation codes.
The platform allows the cooperation and coupling of software modules defined by distributed components on local area networks (LAN), networks of workstations (NOW) and wide area networks (WAN). It uses the CORBA standard for the definition, manipulation and execution of the components defined by distributed objects.
It supports the cooperation, coupling and mixing of both Corba and non-Corba
compliant software modules. This allows for the integration of existing
software, while avoiding costly adaptations to the Corba interface provided
by CAST.






 SHOOD
references
SHOOD
references
 Relax,
take-off :
Relax,
take-off : ...
and go over the mountains !
...
and go over the mountains !

 INRIA
Rhône-Alpes.
INRIA
Rhône-Alpes.

